Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Write a bash script create Directories.sh that when the script is executed with three given arguments (one is directory name and second is start number of directories and third is the end number of directories ) it creates specified number of directories with a dynamic directory name.
Scenario 1: When the script is executed as
./createDirectories.shday 1 90then it creates 90 directories as
day1 day2 day3 .... day90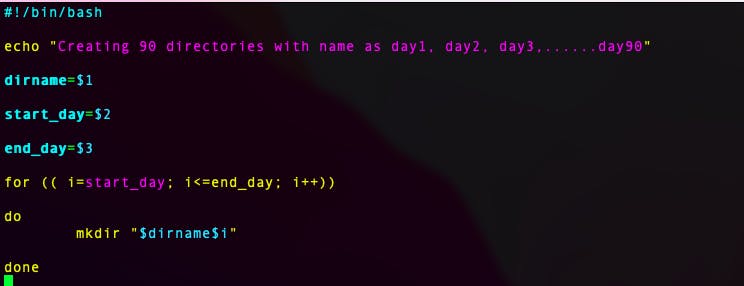
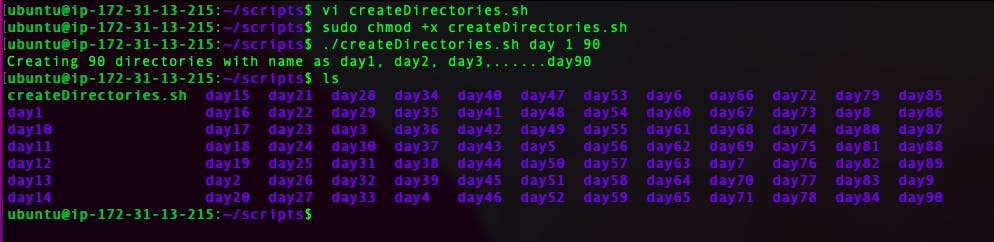
Scenario 2: When the script is executed as
./createDirectories.shMovie 20 50then it creates 50 directories asMovie20 Movie21 Movie23 ...Movie50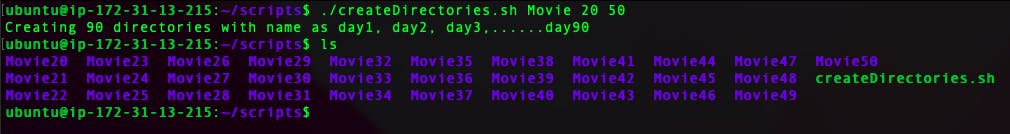
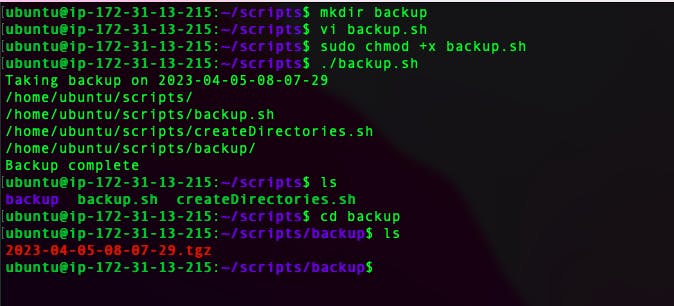
Create a Script to backup all your work done till now.
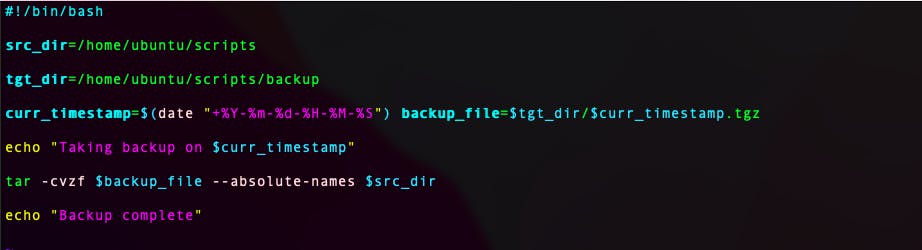
Read About Cron and Crontab, to automate the backup Script
Cron - Cron is a job scheduling utility present in Unix like systems. The crond daemon enables cron functionality and runs in the background. The cron reads the crontab (cron tables) for running predefined scripts.
The scheduled tasks are known as cron jobs while the crontab is the list of the file containing the cron jobs.
Crontab is useful to perform various operations such as handling automated backups, rotating log files, syncing files between remote machines and clearing out temporary folders, etc.
Crontabs use the following flags for adding and listing cron jobs.
crontab -e: edits crontab entries to add, delete, or edit cron jobs.crontab -l: list all the cron jobs for the current user.crontab -u username -l: list another user's crons.crontab -u username -e: edit another user's crons
# Cron job example
* * * * * sh /path/to/script/script.sh
| | | | | |
| | | | | Command or Script to Execute
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | Day of the Week(0-6)
| | | |
| | | Month of the Year(1-12)
| | |
| | Day of the Month(1-31)
| |
| Hour(0-23)
|
Min(0-59)
Read about User Management
User management in Linux is the process of creating, modifying, and deleting user accounts on a Linux system. In Linux, each user has a unique username and password, which are used to log in and access the system.
We can set different permissions for different users in LINUX
adduser: add a user to the system.
passwd: set password of user
userdel: delete a user account and related files.
usermod: modify a user account.
sudo: run commands as superuser permissions.sudo cat /etc/passwd: To check user account properties
su username : For switching user account
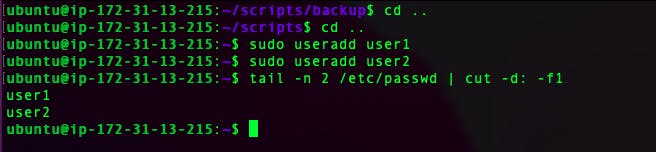
#to add user useradd username #to set password passwd username #to get userid id username #to change user id usermod -u new_id username #to change user name usermod -l new_username old_username #to modify groupid of user usermod -g new_group_id username #to change the home directory usermod -d new_home_directory_path username #to delete user userdel -r usernameCreate 2 users and just display their Usernames
Thank you all for giving your valuable time for reading
stay in touch!! many more blogs in a queue!! Happy Learning
Great initiative by the #trainwithshubham community. Thank you Shubham Londhe for Guiding Us.
